Post summary: Tutorial how to do code coverage with offline instrumentation with JaCoCo and Maven.
Offline instrumentation
Code coverage of manual or automated tests with JaCoCo post describes how to do code coverage with JaCoCo. This is applicable in many of the cases. Still, there could be a case where the application under test does not support Java agents. In this case, JaCoCo offers offline instrumentation of the code. A once instrumented code can be run and coverage to be measured. This post describes how to do it.
JaCoCo for Maven
JaCoCo Maven plugin is discussed in Automated code coverage of unit tests with JaCoCo and Maven post. In order to get code instrumented “instrument” task should be added to Maven:
<properties>
<jacoco.skip.instrument>true</jacoco.skip.instrument>
</properties>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
<artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.7.4.201502262128</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>jacoco-instrument</id>
<phase>test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>instrument</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<skip>${jacoco.skip.instrument}</skip>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
In the current example, this task will be executed when mvn test is called. It can be configured to be called on package or install by changing the <phase> element.
Make it configurable
Instrumentation should not be done on every build. You do not want to release instrumented code, first because this is bad practice and second code will not run unless jacocoagent.jar is in the classpath. This is why instrumentation should be disabled by default with jacoco.skip.instrument=true in pom.xml property, which can be overridden when needed with mvn clean test -Djacoco.skip.instrument=false command. Another option is separate pom-offline.xml file and build with it when needed.
Get sample application
Current post uses sample application first introduced in Build a RESTful stub server with Dropwizard post. It can be found in GitHub sample-dropwizard-rest-stub repository. For the current tutorial, it has been downloaded to C:\sample-dropwizard-rest-stub. This application gets packaged to a single JAR file by mvn clean package. If instrumentation gets put in package phase then it is not working, as packaging happens before instrumentation. This is why test phase is the correct for the current example, as package includes test by default.
Instrument the code
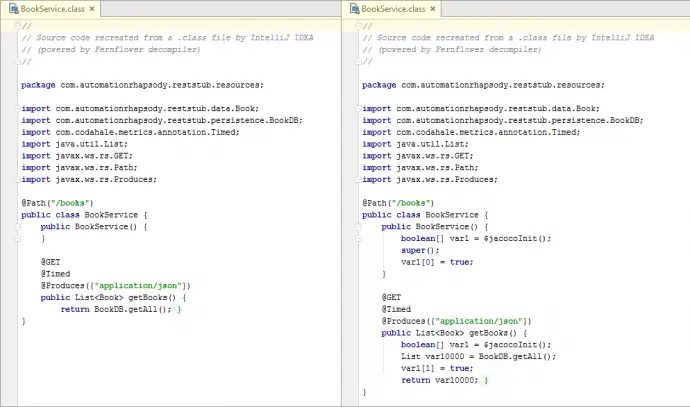
Once the application is downloaded it can be built with instrumentation with mvn clean package -Djacoco.skip.instrument=false command. You can easily check if given class has been instrumented by opening it with some kind of decompiler. The image below shows instrumented class on the right hand side vs non-instrumented in the left hand side.
Run it with JaCoCo agent in the class path
If not instrumented sample application is started with: java -jar target/sample-dropwizard-rest-stub-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar server config.yml. In case of instrumented code this command will give exception:
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/jacoco/agent/rt/internal_773e439/Offline
This is because jacocoagent.jar is not in the classpath.
Adding JaCoCo agent in class path varies from case to case. In this particular tutorial application is a single JAR run by java -jar command. In order to add something in classpath java -cp command should be used. Problem is both -jar and -cp are mutually exclusive. Only way to do it is with the following command:
java -Djacoco-agent.output=tcpserver -cp C:\JaCoCo\jacocoagent.jar;target/sample-dropwizard-rest-stub-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.automationrhapsody.reststub.RestStubApp server config.yml
Where -Djacoco-agent.output=tcpserver is configuration to make JaCoCo agent report on TCP port. More about JaCoCo Offline settings here. C:\JaCoCo\jacocoagent.jar is the location of the JaCoCo agent JAR file. com.automationrhapsody.reststub.RestStubApp is the main method to be run from target/sample-dropwizard-rest-stub-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar file.
Test
Now when we have the application running is time to run all tests we have both automation and manual. For manual, it is important to be documented scenario which is reproducible on each regression testing, not just some random clicking. The idea is that we want to measure what coverage our tests do.
Import coverage results
In order to import results Eclipse with installed JaCoCo plugin from market place is needed. See Code coverage of manual or automated tests with JaCoCo post for more details how to install the plugin.
Open Eclipse and import C:\sample-dropwizard-rest-stub project as Maven one.
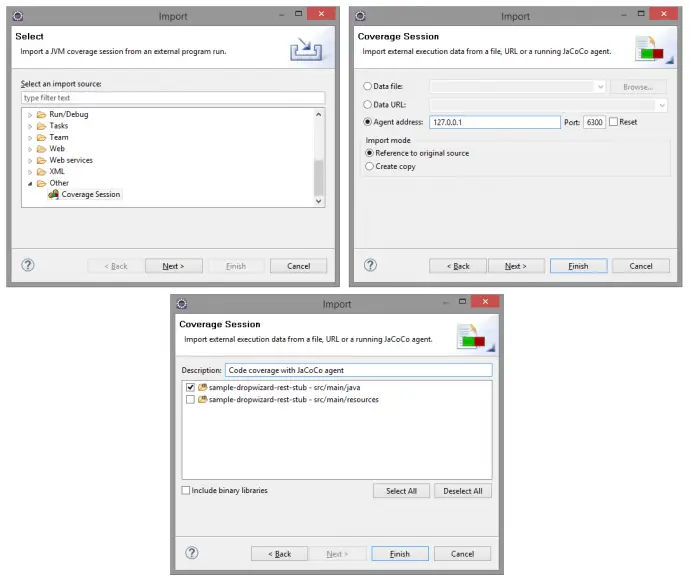
Import the results into Eclipse. This is done from File -> Import -> Coverage Session -> select Agent address radio button but leave defaults -> enter some name and select code under test.
Once imported results can be seen and code gets highlighted.
In case no results are imported delete target\classes folder and rebuild with mvn compile.
Export to HTML and analyze
See Code coverage of manual or automated tests with JaCoCo how to export and analyze.
Conclusion
Although very rare to happen offline instrumentation is a way to measure code coverage with JaCoCo.