Post summary: Templates to be applied to IntelliJ IDEA for automatic generation of toString() method that outputs the object in JSON format.
In some situations like APIs testing, it is good to be able to output requests and responses into log files for easy debugging. In some cases you might work with some framework that receives an object and sends it to the wire, receives the response and give you back object without having the possibility to output the data being sent or received. What you can do is print your request/response objects to logs.
Override toString() method
In order to print essential information from your object, it should properly override toString() method. Default Object.toString() prints full class name with memory address. This gives no information whatsoever. Overriding toString() by hand is not a really good idea as in case of API you have lots of objects.
IntelliJ IDEA toString() automatic generation
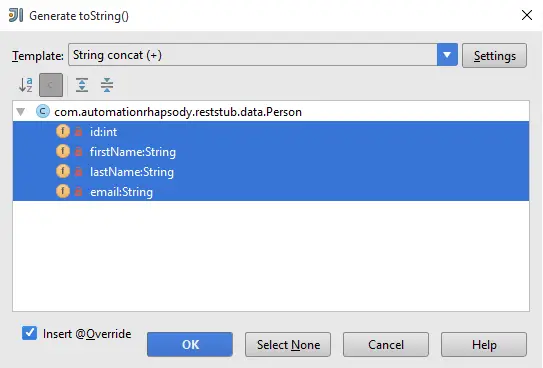
IntelliJ IDEA provides a way to automatically generate toString() method. It can be done by Generate toString() window shown below. Select Template and fields that have to be included then click OK. If there is already toString() method defined there is confirmation if you want to replace existing one.
Generate toString() window is opened either by right click on the object you want to generate toString() for and selecting Generate from the menu, or by keyboard combination Alt + Insert. More about keyboard combinations can be found in IntelliJ IDEA keyboard combinations post.
Custom toString() template
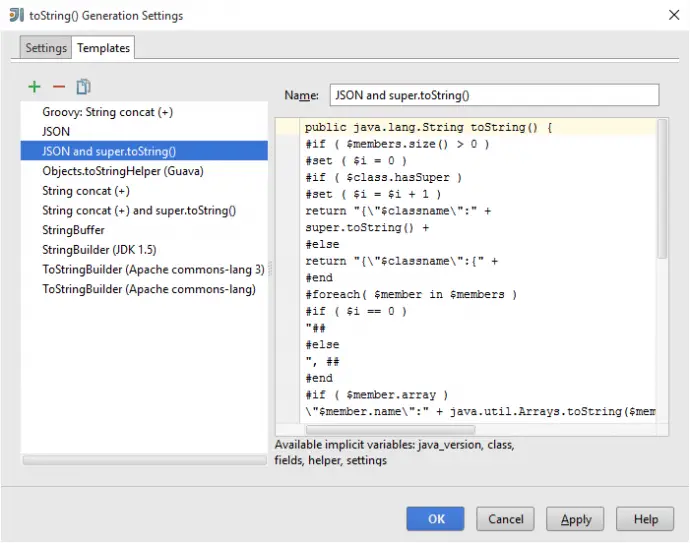
IntelliJ IDEA comes with several predefined templates but none of them can print to JSON. You can customize and build your own template by selecting Settings button from Generate toString() window and then go to Templates tab.
Checkstyle
Checkstyle does static code analysis to verify Java code conforms to specific rules. It has OperatorWrapCheck which requires all operators to be at the beginning of the line. Templates below are created according to this rule. In case plus sign is required to be at the end of the line this can be very easily changed in templates.
JSON toString() template
Below is a toString() template that print object to a valid JSON. It doesn’t include super.toString() method if current class has superclass.
public java.lang.String toString() {
#if ( $members.size() > 0 )
#set ( $i = 0 )
return "{\"$classname\":{"
#foreach( $member in $members )
#if ( $i == 0 )
+ "##
#else
+ ", ##
#end
#if ( $member.array )
\"$member.name\":" + java.util.Arrays.toString($member.accessor)
#elseif ( $member.string || $member.primitive || $member.numeric || $member.boolean || $member.enum )
\"$member.name\":\"" + $member.accessor + "\""
#else
\"$member.name\":" + $member.accessor
#end
#set ( $i = $i + 1 )
#end
+ "}}";
#else
return "{$classname}";
#end
}
JSON toString() template with super.toString() included
Below is a toString() template that print object to a valid JSON. It includes super.toString() method only if current class has super class.
public java.lang.String toString() {
#if ( $members.size() > 0 )
#set ( $i = 0 )
#if ( $class.hasSuper )
#set ( $i = $i + 1 )
return "{\"$classname\":"
+ super.toString()
#else
return "{\"$classname\":{"
#end
#foreach( $member in $members )
#if ( $i == 0 )
+ "##
#else
+ ", ##
#end
#if ( $member.array )
\"$member.name\":" + java.util.Arrays.toString($member.accessor)
#elseif ( $member.string || $member.primitive || $member.numeric || $member.boolean || $member.enum )
\"$member.name\":\"" + $member.accessor + "\""
#else
\"$member.name\":" + $member.accessor
#end
#set ( $i = $i + 1 )
#end
#if ( $class.hasSuper )
+ "}";
#else
+ "}}";
#end
#else
return "{$classname}";
#end
}
Template notation
Template engine uses Apache Velocity. There are a lot of variables that you can use. List of these is shown on Generate toString Setting Dialog page.
Conclusion
This is a handy feature that IntelliJ IDEA provides. Hope you can make use of it.